Lifestyle Diseases: Causes, Impacts, and Prevention Strategies


You likely know that chronic diseases like heart disease, stroke, cancer, and diabetes are among the most common, costly, and preventable of all health problems. What you may not realize is that four modifiable health behaviors – lack of exercise, poor nutrition, tobacco use, and excessive alcohol consumption – are responsible for much of the illness, suffering, and early death related to these lifestyle diseases.
In this article, you will learn about the primary causes of lifestyle diseases, their negative impacts on individuals and society, and evidence-based strategies to prevent these disorders by making simple but impactful changes to daily habits and routines. Equipped with this knowledge, you will be empowered to make choices that significantly reduce your risk and help you live an active, healthy life.
What Are Lifestyle Diseases and Disorders?
Lifestyle diseases, also known as non-communicable diseases, are medical conditions or diseases caused or aggravated primarily due to lifestyle or behavioral factors. Some of the major lifestyle diseases include:
Heart disease and stroke
Heart disease and stroke are the leading causes of death globally. They are caused by unhealthy diet, physical inactivity, tobacco use and harmful use of alcohol. Making positive lifestyle changes can help prevent and manage these diseases.
Cancer
Cancer is a leading cause of death worldwide and the most prevalent lifestyle-related cancer types are lung, colorectal and breast cancers. Exposure to tobacco, unhealthy diet, obesity and physical inactivity are the most common risk factors for developing cancer. Adopting a balanced diet, maintaining a healthy weight and limiting alcohol intake can help lower the risk.
Diabetes
The global diabetes epidemic is linked to overweight and obesity, unhealthy diet and physical inactivity. Type 2 diabetes, the most common form, can often be prevented or delayed by lifestyle changes. Losing excess weight, following a healthy diet and engaging in regular physical activity are effective ways to help prevent or control diabetes.
Chronic respiratory diseases
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma are common chronic respiratory diseases associated with tobacco use, air pollution and occupational chemicals and dusts exposure. Avoiding tobacco products and exposure to air pollutants can help prevent these respiratory conditions.
Common Lifestyle Diseases: Heart Disease, Diabetes, Obesity
Heart Disease
Heart disease refers to several conditions that affect the structure and functions of the heart, including coronary artery disease, high blood pressure, and stroke. The primary cause of heart disease is atherosclerosis, which is the buildup of plaque in the arteries. Plaque is made up of fat, cholesterol, calcium, and other substances found in the blood.
As plaque accumulates in the arteries, the arteries narrow and stiffen, limiting blood flow. This can lead to chest pain, high blood pressure, heart attack, and other complications. The major risk factors for heart disease are smoking, high cholesterol, high blood pressure, physical inactivity, obesity, and diabetes. Making positive lifestyle changes can help prevent and treat heart disease.
Diabetes
Diabetes mellitus refers to a group of diseases that affect how the body produces or uses insulin. Insulin is a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels. In diabetes, the body does not make enough insulin or does not use insulin well, causing glucose to build up in the blood. Over time, high blood sugar levels can lead to serious health problems like heart disease, blindness, and kidney disease.
The two most common types of diabetes are type 1 diabetes, in which the body does not produce insulin, and type 2 diabetes, in which the body does not use insulin effectively. Maintaining a healthy weight, eating well, and exercising regularly can help prevent and manage type 2 diabetes. For type 1 diabetes, insulin injections are required to control blood sugar levels.
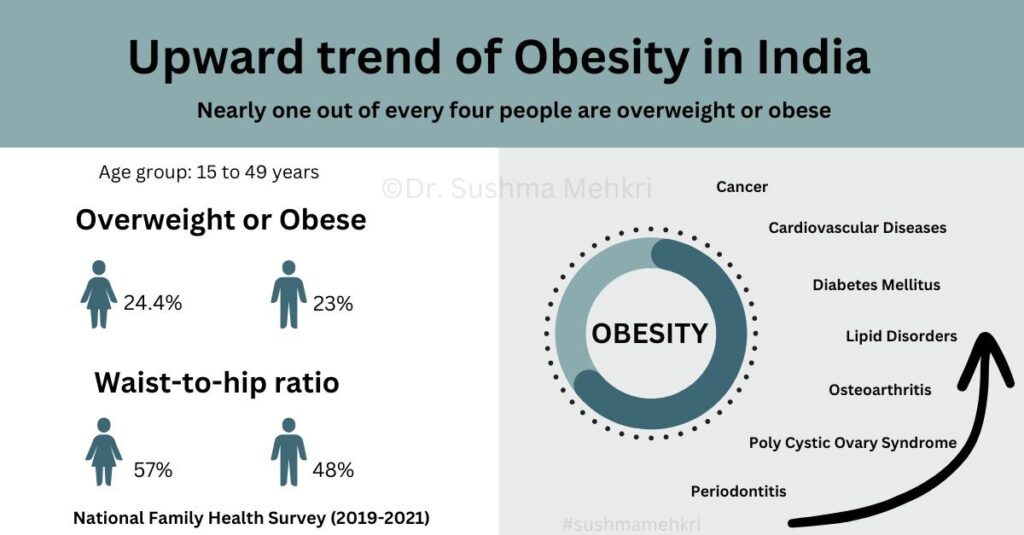
Obesity
Obesity refers to excessive amounts of fat accumulation in the body. It has become a global epidemic and major contributor to chronic health conditions like heart disease, diabetes, and cancer. Obesity is the result of an imbalance between energy intake from the diet and energy expenditure from physical activity and metabolism, Genetics, hormone levels, and certain medical conditions can also influence a person’s weight.
Losing weight and maintaining a healthy weight through improved diet and exercise is the primary strategy for preventing and managing obesity. Even modest weight loss of 5 to 10 percent of total body weight can have significant health benefits.
Causes of Lifestyle Diseases
Poor Diet
Consuming a diet high in calories, fat, sugar and salt but low in nutrients is a major contributor to lifestyle diseases. Eating excess refined carbohydrates, red meat and processed foods can lead to weight gain and obesity. It also increases the risk of diseases like diabetes, heart disease and some cancers. Replacing unhealthy food options with more nutritious choices like fruits and vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help prevent and manage lifestyle diseases.
Physical Inactivity
Lack of regular exercise or physical activity accelerates aging and reduces lifespan. It is a risk factor for obesity, cardiovascular disease, high blood pressure, diabetes, stroke and some forms of cancer. Engaging in at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week can help maintain a healthy weight and significantly reduce health risks. Simple lifestyle changes like walking instead of driving short distances, using stairs instead of elevators, and engaging in active hobbies can provide health benefits.
Smoking
Tobacco use is a major cause of lung diseases, heart disease and various types of cancer. Smoking constricts blood vessels, raises blood pressure and heart rate, and makes blood more likely to clot. It stains the lungs, fingernails and teeth yellow and causes premature aging of the skin. Secondhand smoke also poses risks to non-smokers. The health benefits of quitting smoking begin immediately and continue for life. Quitting will significantly reduce health risks and add years of life.
The Impact of Lifestyle Diseases on Health and Wellbeing
The rise of lifestyle diseases poses a serious threat to human health and wellbeing. These diseases, also known as non- communicable diseases, are linked to unhealthy lifestyles and choices. Examples include heart disease, stroke, diabetes, and certain types of cancer. According to the World Health Organization, lifestyle diseases are the leading cause of death globally, killing 41 million people each year.
Physical Health
Lifestyle diseases often lead to long-term health issues and reduced quality of life. Heart disease and stroke, for instance, can cause cardiac arrest or permanent disability. Diabetes may result in kidney failure, blindness, and limb amputations. Cancer typically requires intensive treatment like surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy which damage healthy cells in addition to eradicating tumors.
Mental Health
In addition to physical effects, lifestyle diseases frequently trigger psychological issues like depression and anxiety. The stress and trauma of diagnosis and treatment, as well as the uncertainty of prognosis, can significantly impact mental health and wellbeing. Financial difficulties from healthcare costs and lost work hours also contribute to worry and distress.
Economic Costs
Lifestyle diseases do not just impact health; they also carry a high economic cost. Healthcare spending on these diseases accounts for over 70% of global health expenditures according to the WHO. Costs are incurred from frequent doctor visits, hospitalizations, procedures, and long-term medication and care. There are also indirect costs from lost productivity when people cannot work due to illness.
The most effective way to curb the threat of lifestyle diseases is through prevention and promotion of healthy lifestyles. Eating nutritious diets, exercising regularly, avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol, and managing stress can help stop these diseases before they start and allow people to lead longer, higher-quality lives. Individuals, communities, and governments must work together to facilitate healthy choices and build environments where the healthy option is the easy option.
Preventing and Managing Lifestyle Diseases Through Lifestyle Changes
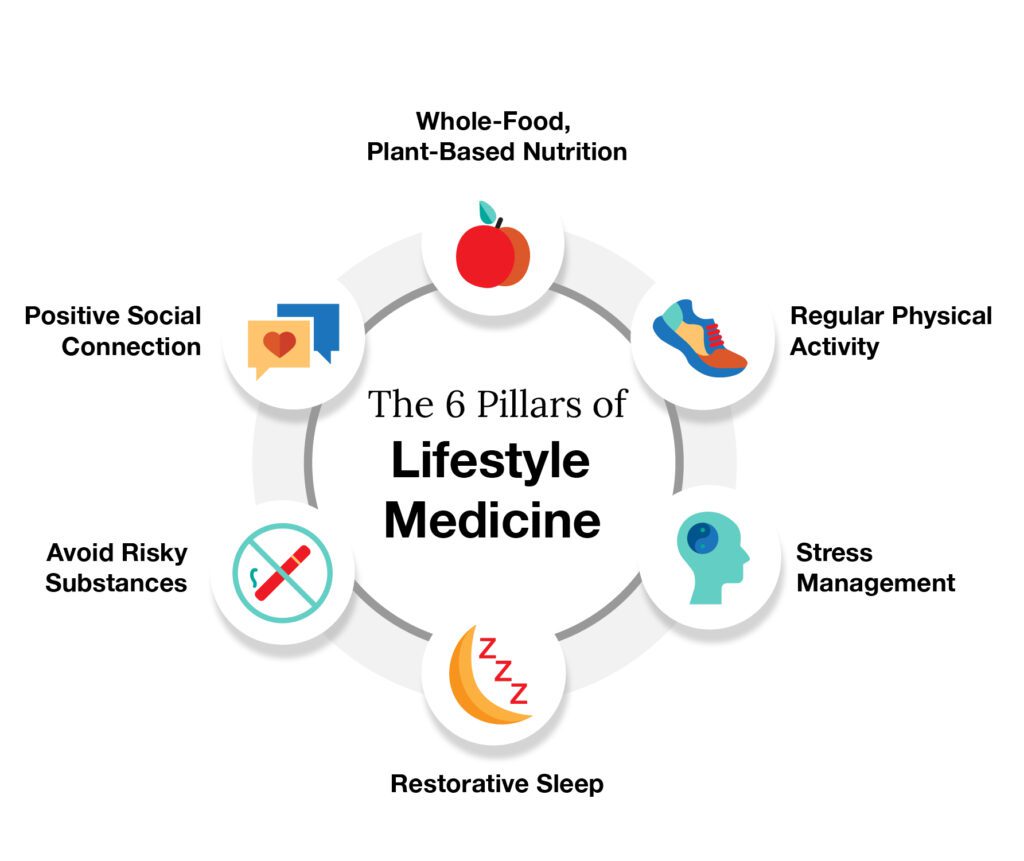
To prevent lifestyle diseases and manage existing conditions, implement positive lifestyle changes. Alterations to diet and exercise are particularly impactful.
Dietary Changes
A balanced diet low in sugar, salt, fat and red meat can help prevent and manage lifestyle diseases. Focus on whole grains, fruits and vegetables, lean proteins. Limit excess sugar, sugary beverages and processed/fast foods. Portion control is also key. These changes help achieve and maintain a healthy weight, control blood pressure/cholesterol, and reduce disease risk.
Exercise Regularly
Exercise lowers disease risk, helps manage weight and improves stamina/flexibility. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate activity most days. Walking, swimming or light strength training are good options. Start slowly and build up as able. Exercise lowers blood pressure/cholesterol, controls blood sugar and boosts metabolism. For those with existing conditions, consult your doctor before beginning an exercise program.
Manage Other Risk Factors
Additional lifestyle changes include:
•Reducing stress through meditation, yoga or deep breathing. High stress contributes to lifestyle diseases.
•Getting adequate sleep. Most adults need 7-9 hours of sleep per night to function optimally. Lack of sleep disrupts hormones and metabolism.
•Avoiding substance abuse. Excessive alcohol or drug use damages health and contributes to disease.
•Practicing good hygiene like brushing/flossing teeth and washing hands frequently. This lowers risks of some infections that may exacerbate lifestyle diseases.
Making permanent lifestyle changes can have significant impacts on both disease prevention and management. While challenging, focusing on balanced diet, regular exercise, stress reduction and limiting unhealthy habits can help add years of healthy life. Consult your doctor for guidance on a customized plan based on your unique health needs.
Conclusion
You now have a deeper understanding of the major lifestyle diseases afflicting society today. By examining their causes and impacts, you can take action to protect your health through prevention strategies like regular exercise, a balanced diet, avoiding tobacco, managing stress, and scheduling annual checkups. While genetics plays a role, many of the risk factors are within your control. Small, consistent lifestyle adjustments add up over time to reduce your chances of developing a condition like heart disease, cancer, or diabetes. Knowledge is power when it comes to your health. Stay vigilant and proactive, and you will be rewarded with better well-being now and in the future.
Don’t let lifestyle diseases control your life! This blog explored the causes and impacts of these chronic conditions, but the power to prevent them lies within you.
The Diet Hub offers a range of Ayurvedic solutions formulated to support your journey towards a healthier lifestyle. Our all-natural products can help manage weight, improve blood sugar control, and promote overall well-being.
Ready to make a change? Visit The Diet Hub today and discover how Ayurveda can empower you to prevent and even reverse lifestyle diseases. Let’s embrace a healthier future, together!